The probability of stochastic radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... effects depends not only on the absorbed doseThe absorbed dose D is the quotient of the average energy tr..., but also on the type and energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... of the radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... causing the doseMeasure of a radiation effect to be indicated more precisely.... This is considered by weighting the absorbed doseThe absorbed dose D is the quotient of the average energy tr... with a factor related to the radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... quality. In the past this factor was known as the quality factorTerm of radiation dosimetry. The quality factor was introduc.... For photonEnergy quantum of electromagnetic radiation. The rest mass o... and electronElementary particle with a negative electrical elementary ch... radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics..., the radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... weighting factorSee tissue weighting factor. has the value 1 independently of the energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... of the radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... and for alpha radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... the value 20. For neutronUncharged elementary particle with a mass of 1.67492716 ·10... radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics..., the value is energy-dependent and amounts to 5 to 20.
Radiation type and energy |
RadiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... weighting factorSee tissue weighting factor. WRSymbol for roentgen |
| Photons, all energies |
1 |
| Electrons, myons, all energies |
1 |
| Neutrons
< 10 keVKiloelectron volt; 1 keV = 1,000 eV; See 'Electron volt'. |
5 |
| Protons > 2 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV. |
5 |
| Alpha particles, fissionSee 'nuclear fission'. fragments, heavy nuclei |
20 |
RadiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... weighting factorSee tissue weighting factor. WR in accordance with Euratom basic standards 1996
The numerical values indicated above are valid legal EU-regulations for calculating the equivalent doseMeasure of a radiation effect to be indicated more precisely... in an organ or tissue. In 2007 ICRPSee 'International Commission on Radiological Protection'. published a new set of radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... weighting factors (ICRPSee 'International Commission on Radiological Protection'. Publ. 103: The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological ProtectionThe "International Commission on Radiological Protection", w...) given below. These data are adopted in the proposal of the new EU Basic Safety Standards (European Commission, Proposal for a Council Directive laying down basic safety standards for protection against the dangers arising from exposure to ionising radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics..., COM(2012) 242 final 2012-05-30 to be accepted by the Council of the European Union eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2012:0242:FIN:EN:PDF
Radiation type |
RadiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... weighting factorSee tissue weighting factor. WRSymbol for roentgen |
|
Photons, all energies |
1 |
|
Electrons, myons, all energies |
1 |
|
Protons and charged pions |
2 |
|
Alpha particles, fissionSee 'nuclear fission'. fragments, |
20 |
|
Neutrons |
A continuous function of neutronUncharged elementary particle with a mass of 1.67492716 ·10... energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... (see equation) |
RadiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... weighting factors (ICRPSee 'International Commission on Radiological Protection'. 2007)
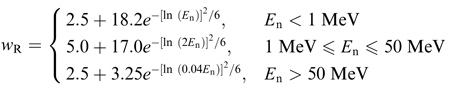
Continuous function in neutronUncharged elementary particle with a mass of 1.67492716 ·10... energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th..., En (MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV.),
for the calculation of radiationEnergy dispersion through matter or space. In atomic physics... weighting factors for neutrons
